Solar storage overview
Types of solar storage system
Grid tied – the system is connected to a mains connection – the National Grid.
Off grid – the system in not connected to a mains connection.
Storage – stores energy so it can be used in the evenings.
Back-up (essential loads only) – stores energy so it can be used in the evenings provides energy to essential loads in your home when there is a power cut.
- Backup (all loads) – stores energy so it can be used in the evenings provides energy to all loads in your home when there is a power cut.
Uninterrupted power supply (UPS) – Changes over from grid electricity to battery electricity fast enough so devices such as computers are not impacted.
DC vs AC coupled solar storage systems
DC coupled means the battery is attached to the DC side of the system – between the solar panels and the solar inverter.

Advantages of DC coupled systems
Easier to install
Do no need prior approval from Distribution Network Operator (DNO)
Simple and low maintenance
Typically less expensive
Disadvantages of DC coupled systems
Not paid feed-in tariffs for the losses on the DC side of the system, which can be as much as 10%
No power to home in event of power cut. Although not an important factor in most UK scenarios where the grid is relatively stable
Solar stops charging batteries in event of power cut
Some systems are not compatible with multi-string PV systems
System design
The systems below are types of AC coupled systems.
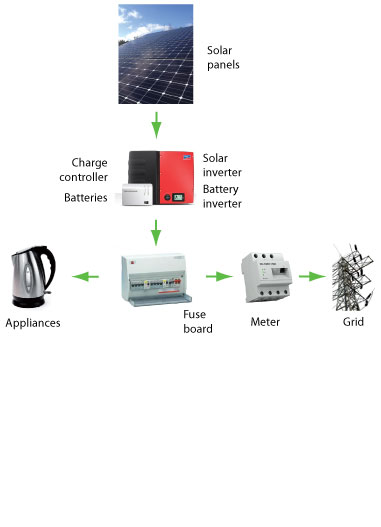
Separate components
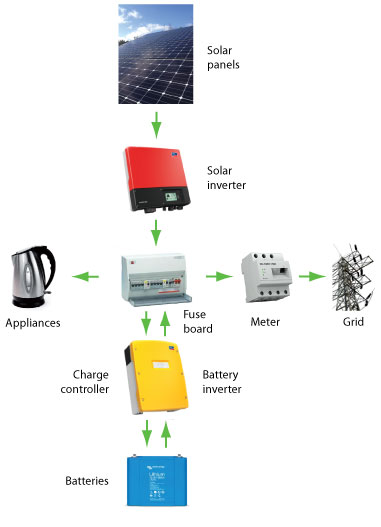
Semi-integrated
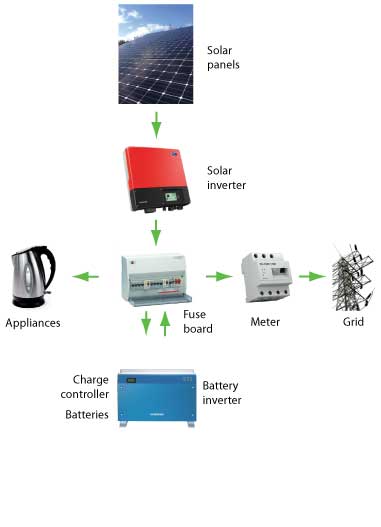
Fully-integrated